| Diagnosis |
|
As thorough a caries diagnostic examination as the child's
level of cooperation permits should be performed. |
D |
The use of bitewing radiography for caries
diagnosis should be considered fro pre-school children attending for dental
care, particularly if they are assessed as being at risk of dental caries.
The timing of subsequent radiographic examinations should be based on
the patient's caries risk status. |
B |
Caries should be diagnosed as early as
possible to allow management before cavitation and pulpal involvement,
and to identify caries-active patients and those at increased risk of
caries in the future. |
C |
Practitioners should receive training
in clinical and radiographic caries diagnosis. |
| |
|
Predicting
Caries Risk |
C |
A dental practice-based caries risk assessment
should be carried out on individual pre-school children and should include
the following risk indicators:
- evidence of previous caries experience
- resident in a deprived area
- healthcare worker's opinion
- oral mutans streptococci counts (if accessible)
|
B |
Children whose families live in a deprived
area should be considered as at increased risk of early childhood caries
when developing preventive programmes.. |
| |
|
| Toothbrushing
with Fluoride Toothpaste |
A |
Children should have their teeth brushed
with fluoride toothpaste containing 1000 +/- 10% ppm F. |
C |
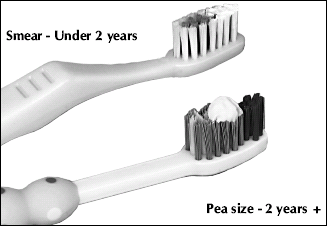
Children should have their teeth brushed,
or be assisted with toothbrushing by an adult, at least twice a day, with
a smear or pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste. |
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
C |
Toothbrushing should be started as soon
as the primary teeth erupt. |
A |
Children should be encouraged
to spit out excess toothpaste and not rinse with water post-brushing. |
A |
Children's teeth can be brushed with either
manual or powered toothbrushes. |
Diet
and Nutrition |
B |
Pregnant women should be advised that
there is no benefit to the child of them taking fluoride tablets during
pregnancy. |
C |
Members of the dental team should support
and promote breastfeeding according to current recommendations. |

|
Parents and carers should be advised that soya infant formulae
are potentially cariogenic and should be used only when medically indicated. |

|
Parents and carers should be advised not to put children
to bed with a bottle of feeder cup. |
|
B
|
Parents and carers should be advised that
foods and confectionery containing free sugars should be minimised and,
if possible, restricted to meal times. |
|
C
|
Parents and carers should be advised that
drinks containing free sugars, including natural fruit juices, should
be avoided between meals and should never be put in a feeding bottle.
Water or milk may be given instead. |
|
C
|
Parents and carers should be advised that
cheese is a good high energy food for toddlers as it is non-cariogenic
and may be actively protective against caries. |
|
B
|
Parents and carers should be advised that
confectionery and beverages containing sugar substitutes are preferable
to those containing sugars. |

|
Parents and carers should be assured that sugar-free snacks
are unlikely to be cariogenic. |
| |
|
| Practice-based
Management |
|
D
|
Primary teeth with caries
progressing into dentine should be actively managed with a preventive
or a preventive and restorative approach, as appropriate with the child's
ability to cooperate. |
|
B
|
If complete caries removal from a vital
primary molar is not possible, an indirect pulp capping technique should
be considered. |
|
B
|
When preparing a Class II cavity, care
must be taken to avoid iatrogenic damage to adjacent proximal tooth surfaces. |
|
B
|
Use of the ART approach for cavity preparation
in carious primary teeth should be considered as an alternative, where
appropriate, to conventional cavity preparation techniques. |
|
A
|
Amalgam, composite, resin-modified glass-ionomers,
compomer, or pre-formed metal crowns should be used as restorative materials
for Class II cavities in primary molars.
Conventional glass-ionomer should be avoided, where possible, for Class
II cavity restoration. |
| |
| Practice-based
Prevention |
|
B
|
The dental team should deliver caries prevention strategies
in conjunction with physical prevention techniques such as the use of
fluoride. |
|
B
|
Parents and their pre-school children should receive oral
health education from their dental team. This should include oral hygiene
instruction, the appropriate use of fluoride toothpaste, and the provision
of fluoride agents such as toothpaste. |
|
B
|
Topical fluoride varnish should be applied to
the dentition at least twice yearly for pre-school children assessed as
being at increased risk of dental caries. |
| |
|
| Community-based
Prevention |
|
A
|
Community of home-based oral health promotion
interventions should use fluoride containing agents such as fluoride toothpaste. |
|
A
|
Community-based toothbrushing programmes
should include fluoride toothpaste with a concentration of 1000 ppm F. |
|
B
|
Toothbrushing programmes should be undertaken:
- in community-based settings such as nurseries
- with parents to create a supportive environment for oral health
behaviour.
|
|
D
|
Oral health promotion programmes to reduce
the risk of early childhood caries should be available for parents during
pregnancy and continued postnatally.
Programmes for young children should be initiated before the age of three
years. |
|
C
|
The oral health of young children should
be promoted through multiple interventions and multi-sessional health
promotion programmes for parents. |
|
C
|
Teachers, community workers, and lay or
peer educators can be effective in delivering health promotion interventions
and their role should be considered in the development of oral health
promotion programmes. |
|
C
|
Professionals should ensure oral health
messages are relevant and applicable to communities and lifestyles. |
|
B
|
Caries prevention measures should target
'at-risk' populations and individuals to reduce oral health inequalities. |
|
D
|
Fluoride supplements should only be prescribed
by dental practitioners on an individual patient basis.. |